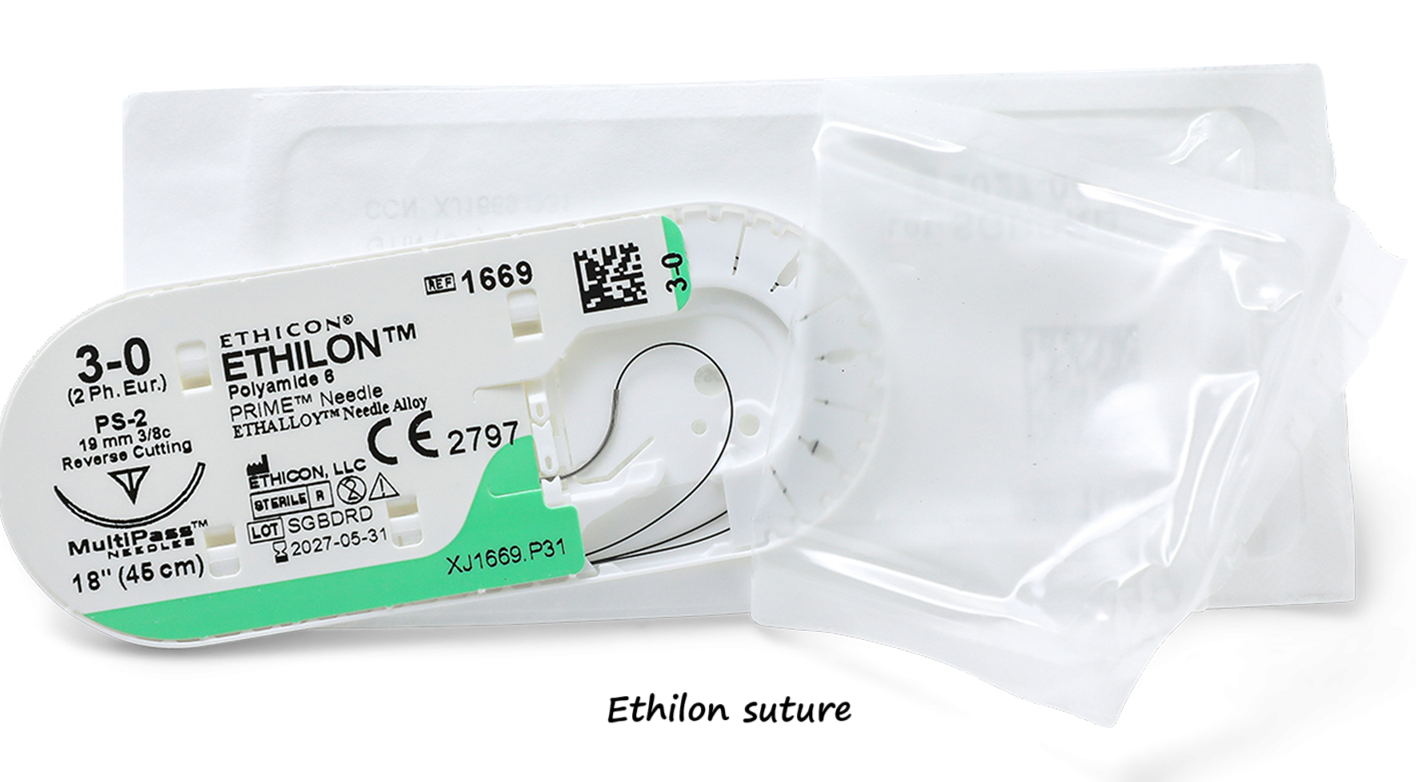
In the world of surgical sutures, choosing the right material is crucial for ensuring optimal wound healing and patient outcomes. Among the many options available, Ethilon sutures have gained widespread recognition for their reliability and versatility. But what exactly are Ethilon sutures, and why are they so commonly used? In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Ethilon sutures, including their features, applications, advantages, and more.
What Are Ethilon Sutures?
Ethilon sutures are a type of non-absorbable, monofilament suture made from polyamide, commonly known as nylon. Manufactured by Ethicon (a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Ethilon sutures are known for their high tensile strength, flexibility, and minimal tissue reaction. These sutures are widely used in various surgical procedures where long-term wound support is required.
Key Features of Ethilon Sutures
- Non-Absorbable: Ethilon sutures are not absorbed by the body, making them ideal for situations where prolonged wound support is needed.
- Monofilament Structure: Unlike braided sutures, Ethilon sutures are made from a single strand of nylon, which reduces the risk of infection and minimizes tissue drag.
- High Tensile Strength: Ethilon sutures provide excellent strength, ensuring secure wound closure even under tension.
- Minimal Tissue Reaction: The inert nature of nylon makes Ethilon sutures biocompatible, causing minimal irritation or inflammation in the surrounding tissues.
- Versatility: Ethilon sutures are available in a wide range of sizes and can be used for various surgical applications.
Applications of Ethilon Sutures
Ethilon sutures are used in a variety of surgical procedures, including:
- Skin Closure: Commonly used for closing skin incisions in general surgery, plastic surgery, and dermatology.
- Ophthalmic Surgery: Ideal for procedures requiring fine, non-absorbable sutures, such as cataract surgery or corneal repairs.
- Cardiovascular Surgery: Used in vascular anastomosis and other procedures requiring strong, durable sutures.
- Orthopedic Surgery: For securing soft tissues and tendons in orthopedic procedures.
- Dental Surgery: Used in oral and maxillofacial surgeries for precise wound closure.
Advantages of Ethilon Sutures
- Durability: Ethilon sutures provide long-term wound support, making them suitable for procedures where absorbable sutures are not ideal.
- Smooth Handling: The monofilament structure ensures smooth passage through tissues, reducing trauma and discomfort.
- Low Infection Risk: The single-strand design minimizes the risk of bacterial colonization compared to braided sutures.
- Biocompatibility: Ethilon sutures are well-tolerated by the body, with minimal risk of allergic reactions or tissue irritation.
- Ease of Removal: While Ethilon sutures are non-absorbable, they can be easily removed once the wound has healed.
Potential Limitations
While Ethilon sutures offer numerous benefits, they may not be suitable for all situations. For example:
- They require removal after the wound has healed, which can be inconvenient for some patients.
- The monofilament structure can make knot tying slightly more challenging compared to braided sutures.
- They may not be ideal for tissues that require absorbable sutures, such as internal organs.
Ethilon vs. Other Sutures
- Ethilon vs. Vicryl: Vicryl sutures are absorbable and often used for internal tissues, while Ethilon is non-absorbable and preferred for skin closure and long-term support.
- Ethilon vs. Prolene: Both are non-absorbable monofilament sutures, but Prolene (made from polypropylene) is often used in cardiovascular surgeries, while Ethilon is more commonly used for skin and ophthalmic procedures.
- Ethilon vs. Silk: Silk sutures are braided and provide better knot security but have a higher risk of infection compared to Ethilon’s monofilament design.
Tips for Using Ethilon Sutures
- Choose the Right Size: Select the appropriate suture size based on the tissue type and surgical site.
- Handle with Care: Avoid excessive tension when tying knots to prevent suture breakage.
- Use Proper Technique: Ensure smooth passage through tissues to minimize trauma.
- Monitor Healing: While Ethilon sutures are non-absorbable, it’s important to monitor the wound for signs of infection or delayed healing.
Conclusion
Ethilon sutures are a trusted choice for surgeons worldwide, offering a combination of strength, durability, and biocompatibility. Whether you’re closing a skin incision or performing delicate ophthalmic surgery, Ethilon sutures provide reliable performance and excellent patient outcomes. As with any medical product, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best suture material for your specific needs.
Have you or someone you know had experience with Ethilon sutures? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you found this post helpful, don’t forget to share it with others who might benefit from this information.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for medical guidance.


Leave a Reply